Key Considerations When Installing Industrial Wireless
Wireless network downtime at home or in the office will be an inconvenience until a replacement device is installed. Wireless network failure in industrial applications, however, can jeopardize the safety of on-site personnel, damage expensive machinery or equipment, and possibly translate into production losses to the tune of thousands of dollars per minute. When installing a wireless network for industrial use, the requirements are definitely different from those for commercial use. Here are the key criteria to consider in industrial wireless networks to ensure good quality connections for reliable and stable networks.
Industrial Design to Tackle Hazardous Environments
Many industrial wireless applications, such as those for mining, railway, and oil and gas, are deployed in harsh environments and require the use of industrial-grade devices. While some environmental factors are obvious, such as extreme temperatures and moisture, there are other not-so-apparent elements that can quickly disable an unprotected device. Here are several examples of interferences and environmental difficulties that are commonly seen in industrial applications.
Electrical Interference
The many different kinds of electrical interferences in an industrial environment include electrostatic discharge accumulated on a human body, surge caused by indirect lightning strikes, and bursts generated by factory generators. Failing to properly design your system to protect against such interference can result in unstable communications, or sometimes permanent damage to your device, causing a complete shutdown of your system. In addition to network redundancy, industrial operators must also assess the application environment for elements that can impact network performance, compromise device reliability, and lead to unplanned system downtime.
Industrial-grade devices are specifically designed so that the internal components and circuits are able to withstand different types of interference. In addition, the manufacturer will test the products to make sure they can operate reliably in harsh conditions so end users can rest assured that the products will be more stable, more reliable, and have a longer life than non-industrial products.

 Radiated Electromagnetic Interference Radiated Electromagnetic Interference
Radiated electromagnetic interference is most obvious near an electrical substation. The high voltage and strong current flow cause a coupling effect on nearby electrical devices. If the devices are not properly protected, the internal circuits of the devices can wear out more quickly or be permanently damaged. The same effect can also be seen near factory generators and large transformers. A good metal casing and properly designed isolation protection in industrial-grade devices can overcome such interference.
 Extreme Temperatures Extreme Temperatures
Under a hot summer sun, devices locked inside an outdoor cabinet can easily reach a temperature of 70°C (158°F), whereas a similar cabinet located at a high altitude could experience a temperature of -30°C (-22°F) on a cold winter night. Without a proper design, electronic devices inside the cabinet could either overheat, or be unable to boot up if the temperature is too low. Two major design considerations for industrial-grade products are heat-dissipation and low-temperature operation. By selecting the right components and mechanical design, engineers can ensure that devices will be able to operate reliably in both extremely hot and extremely low temperatures.
 Shock and Vibration Shock and Vibration
Wireless technology is widely used in mobile communications. However, for devices installed in vehicles with RJ45 connectors and/or standard power jacks, the continuous vibration of the vehicle can cause the connections to wiggle loose. In order to provide a more reliable connection, industrial products designed for mobile communications often come with M12 connectors for data communication and terminal blocks for power and DI/DO connections.
Robust Wireless Design to Ensure Stability and Reliability
A key requirement in all industrial applications is seamless connectivity and performance of the wireless network. There simply cannot be any downtime.
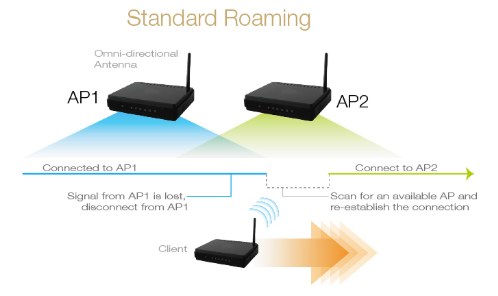
Quick Roaming Recovery Time
Recent advances in wireless technology have made it possible to use wireless for mission-critical mobile applications, such as railway (Train-to-Ground), buses (wayside AP communication), and automated guided vehicles in factories. The most crucial aspect of these mission-critical wireless applications is ensuring uninterrupted communication between wireless clients and access points (AP), even when the wireless client is roaming at considerable speeds between different APs. The different types of roaming that industrial wireless devices support are standard roaming, client-based roaming, and controller-based roaming.
Anti-Interference Techniques
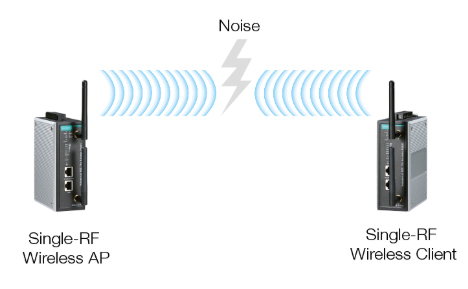
The rapid advancement of wireless technology has led to an increase in wireless deployments around the world. In order to prevent Wi-Fi equipment from interfering with each other, many standards and mechanisms have been set up, including collision avoidance (CDMA-CA), communication control (RTS/CTS), and Inter Frame Spacing (IFS). However, even when these mechanisms are working perfectly, instability in wireless connections caused by a lack of 802.11 radio signals, or co-channel or adjacent-channel interferences can occur. Many approaches are available to overcome these problems.
Auto Channel Assessment and Adjustment
One commonly known approach is auto channel assessment and adjustment. This approach examines the current channel to determine its quality. When the current connection fails the examination, the device will automatically switch to a cleaner channel. However, channel adjustment and renegotiation can still result in packet loss and is unacceptable for latency-intolerant applications.
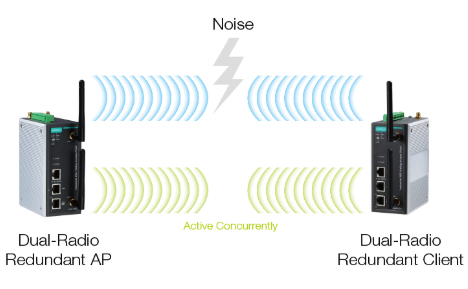
Dual Channel Wireless Redundancy
For mission-critical applications, higher reliability and stability is required. Zero-packet-loss wireless communication can be achieved, using concurrent dual-radio transmission, to provide highly reliable wireless connectivity for safety-critical applications, with benefits such as optimized data throughput, interference immunity, and latency-free transmissions.
Moxa Solutions
As more and more industrial applications use industrial wireless, it is important to understand what is best for your requirement. One solution can’t fit all. To get a more comprehensive understanding of the wireless landscape, industrial wireless technologies, and related industry standards, download Moxa's Definitive Industrial Wireless Guidebook. |

 Radiated Electromagnetic Interference
Radiated Electromagnetic Interference Extreme Temperatures
Extreme Temperatures Shock and Vibration
Shock and Vibration

